Kubernates Operational and Verification Command
Check node, version, name
kubectl get node
kubectl get node -o wide
kubectl version
Verify node detail
kubectl describe node <NODE NAME>
Verify resources available
kubectl api-resources
Use for api/resource detail check
kubectl explain <RESOURCE>
Get namespaces
kubectl get namespace
Get all pods on all namespace
kubectl get pods –all-namespaces
Running a single pod
kubectl run pingpong –image alpine ping 1.1.1.1
kubectl run webapp –image nginx
Remove Pods
kubectl delete pods webapp
Running a deployment
kubectl create deployment deployment-1 –image=alpine — ping 1.1.1.1
Create a deployment
kubectl create -f app.yml
kubectl apply -f app.yml
Scale deployment to 3
kubectl scale deployment deployment-1 –replicas 3
Check pod logs
kubectl logs pingpong
kubectl logs pingpong –tail 1 –follow
Check Service on Cluster
kubectl get service
Get Service Detail
kubectl describe service [SERVICE,DEPLOYMENT]psi-admin@mickrok8s-1:~$ kubectl describe service httpenv
Name: httpenv
Namespace: default
Labels: app=httpenv
Annotations:
Selector: app=httpenv
Type: ClusterIP
IP Family Policy: SingleStack
IP Families: IPv4
IP: 10.152.183.234
IPs: 10.152.183.234
Port: 8888/TCP
TargetPort: 8888/TCP
Endpoints: 10.1.156.10:8888,10.1.156.11:8888,10.1.156.12:8888 + 7 more…
Session Affinity: None
Events:Endpoint list that shows above are actually the POD
Headless Service

kubectl expose deploy my-little-deploy --cluster-ip=None --port=80 Run a pod every 3 minutes
kubectl run --schedule=*/3 * * * * pingpong --image alpine ping 1.1.1.1#it is cron time, which each * is minutes[0-59] hour[0-23] dayofmonth[1-31] monthofyear[1-12] dayofweek[0-6,0=sunday]Exposing Port to Deployment/Pod, ie expose port 8888 to deployment=httpenv
kubectl expose deployment httpenv --port 8888
#when exposing, the service is created for it. To un-expose or remove expose
kubectl delete service httpenvSHPOD install, for testing pod from internal IF we are using non-linux Controller
kubectl apply -f https://bret.run/shpod.ymlRun a console to SHPOD
kubectl attach --namespace=shpod -ti shpodSample yaml file for creating pods
Create yml from external deployment
kubectl get deploy/rng -o yaml >rng.ymlSelector and Label, using describe we can see a label for a service and what filter it is used to choose back end pods.
psi-admin@microk8s-2:~$ kubectl describe service rng
Name: rng
Namespace: default
Labels: app=rng
Annotations: <none>
Selector: app=rng
Type: ClusterIP
IP Family Policy: SingleStack
IP Families: IPv4
IP: 10.152.183.174
IPs: 10.152.183.174
Port: <unset> 80/TCP
TargetPort: 80/TCP
Endpoints: 10.1.100.139:80,10.1.100.153:80
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>Verify/list pods based on selector(filter based on selector) can be done using -l
psi-admin@microk8s-2:~$ kubectl get pods -l app=rng
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
rng-7c7c6c8d74-vt55b 1/1 Running 0 5h18m
rng-vljzk 1/1 Running 0 5m21sLabel and Selector
Check current label
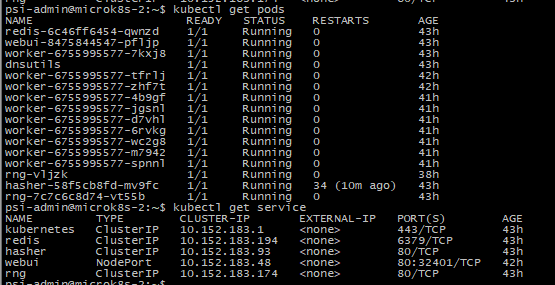
kubectl desribe pod deployment
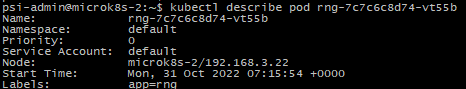
kubectl desribe pod daemonset
Both has the same label, but we can check the pod-template are different below:
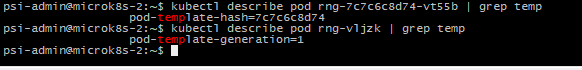
The pod-template-hash ==> replicaset or deployment
The pod-template-generation ==> daemonset
To add new label
kubectl label pods -l app=rng enabled=yesEditing the service to filter the correct/new label
kubectl edit service rngLook for label in the spec section
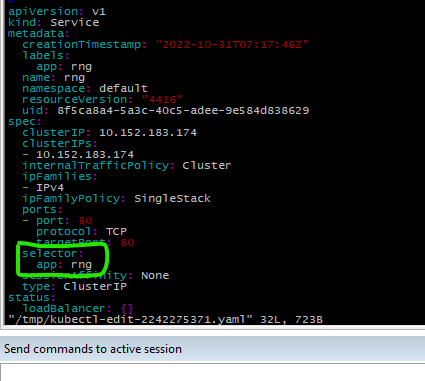
Edited to:
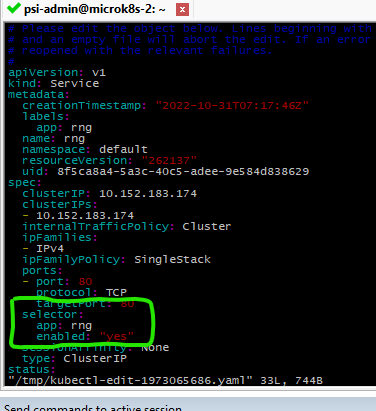
Remove label enabled from only the deployment pod (has attribute pod-template-hash), keep the pod running and set only daemon sets pod active in service
kubectl label pod -l app=rng,pod-template-hash enabled-enable- = remove label enable
Create a sample kubernates YAML file without disrupting the system
Create Deployment WEB with NGINX to output as yaml file
kubectl create deployment WEB --image nginx -o yaml --dry-runCreate Deployment WEB with NGINX to output as yaml file but SHORT yaml
kubectl create namespace SAMPLE -o yaml --dry-run
