Install Cluster Kubernetes using Kubeadm Ubuntu 22.04, Kubeadm Cluster 1.31, Calico 3.29
Requirement :
- 3 machines running Ubuntu 22.04 – Jammy
- master-1
- worker-1
- worker-2
- 4 GiB or more of RAM per machine–any less leaves little room for your apps.
- At least 2 CPUs on the machine that you use as a control-plane node.
- Full network connectivity among all machines in the cluster. You can use either a public or a private network.
Initialize node
reference : https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/production-environment/container-runtimes/#containerd
Make sure date time are correct and synced
We use timesyncd, check the status
systemctl status systemd-timesyncdEdit your NTP Server
root@node1:/home/chairul# cat /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf
[Time]
NTP=[NTP Server]Restart the service
systemctl restart systemd-timesyncdCheck your time and timezone, set your timezone if neccessary
$timedatectl
$timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Jakarta
Remove Swap
$strace -eopenat kubectl version
#swapoff -a
#sudo sed -i '/\tswap\t/d' /etc/fstabSometime etcd having problem running in Ubuntu 22.04, edit the grub config,, edit a line
#cat /etc/default/grub
…
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=”systemd.unified_cgroup_hierarchy=0″
…
Disable AppArmor
sudo systemctl stop apparmor && sudo systemctl disable apparmor
iptables -FFor all Node, run as root
#apt updateInitialize the node parameter
#cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
$sudo modprobe overlay
$sudo modprobe br_netfilter
### sysctl params required by setup, params persist across reboots
#cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 1000000
EOF
### Apply sysctl params without reboot
$sudo sysctl --system
### Verify
#lsmod | grep br_netfilter
#lsmod | grep overlay
#sysctl net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables net.ipv4.ip_forward
#Sample Output
root@master-1:/home/ubuntu# lsmod | grep br_netfilter
br_netfilter 32768 0
bridge 311296 1 br_netfilter
root@master-1:/home/ubuntu# lsmod | grep overlay
overlay 151552 25
root@master-1:/home/ubuntu# sysctl net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables net.ipv4.ip_forward
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
root@master-1:/home/ubuntu#Install Containerd
Reference: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/
For all nodes :
Update package
$sudo apt updateSetup the Repository
# Add Docker's official GPG key:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
# Add the repository to Apt sources:
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install containerd.ioUse correct cgroup
#Verify cgroup drivers
$sudo ps -p 1
root@master-1:/home/ubuntu# sudo ps -p 1
PID TTY TIME CMD
1 ? 00:00:01 systemdIf it systemd, config the cgroup driver:
Edit /etc/containerd/config.toml. Make it to default value
sudo mkdir -p /etc/containerd
sudo containerd config default | sudo tee /etc/containerd/config.tomlReplace systemdcgroup, with this following
sudo nano /etc/containerd/config.toml
...
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc.options]
SystemdCgroup = true
...Make sure crictl info returning the info, not error.
#crictl info
root@coba-coba:/home/ubuntu# crictl info
WARN[0000] runtime connect using default endpoints: [unix:///run/containerd/containerd.sock unix:///run/crio/crio.sock unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock]. As the default settings are now deprecated, you should set the endpoint instead.
{
"cniconfig": {
"Networks": [
{
"Config": {
"CNIVersion": "0.3.1",
"Name": "cni-loopback",
"Plugins": [
{
"Network": {Setup kernel parameter for containerd
#mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/containerd.service.d
#cat <<EOF | tee /etc/systemd/system/containerd.service.d/override.conf
[Service]
LimitMEMLOCK=4194304
LimitNOFILE=1048576
EOF
#cat > /etc/modules-load.d/containerd.conf <<EOF
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
#systemctl daemon-reload
#systemctl restart containerdInstalling kubeadm, kubelet and kubect
Reference : https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/install-kubeadm/
Do this on all nodes
Update the apt package index and install packages needed to use the Kubernetes apt repository:
$sudo apt-get update
### apt-transport-https may be a dummy package; if so, you can skip that package
$sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl
Download the public signing key for the Kubernetes package repositories. The same signing key is used for all repositories so you can disregard the version in the URL:
# If the directory `/etc/apt/keyrings` does not exist, it should be created before the curl command, read the note below.
# sudo mkdir -p -m 755 /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.31/deb/Release.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
Add the appropriate Kubernetes apt repository:
# This overwrites any existing configuration in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
echo 'deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.31/deb/ /' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.listUpdate the apt package index, install kubelet, kubeadm and kubectl, and pin their version:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectlDeploy the cluster
Do this on the Master node
Get the IP address of the Master main interface/adapter of the controlplane
ip a
root@master-1:/home/ubuntu# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether fa:16:3e:b7:9b:bd brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp0s3
inet 10.5.24.32/24 metric 100 brd 10.5.24.255 scope global dynamic ens3
valid_lft 41773sec preferred_lft 41773sec
inet6 fe80::f816:3eff:feb7:9bbd/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft foreverSet the master hostname to be resolve locally to the listener IP
root@master-1:/home/ubuntu# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
10.5.24.32 master-1
10.5.24.165 worker-1
10.5.24.181 worker-2
::1 ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
ff02::3 ip6-allhostsInitialize the Kubernates Master with the IP
$sudo kubeadm init \
--apiserver-cert-extra-sans=master-1\
--control-plane-endpoint 10.5.24.32\
--pod-network-cidr=192.168.0.0/16
### If encountering [preflight] Some fatal errors occurred:
failed to create new CRI runtime service: validate service connection: validate CRI v1 runtime API for endpoint "unix:///var/run/containerd/containerd.sock", Error
#### Refer to this https://forum.linuxfoundation.org/discussion/862825/kubeadm-init-error-cri-v1-runtime-api-is-not-implemented
###at the final output you should get this
==========================================
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of control-plane nodes by copying certificate authorities
and service account keys on each node and then running the following as root:
kubeadm join 10.5.24.32:6443 --token 4639jr.a7smqg4qwzp3tv2u \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:70b896b391bc1956dfbf6b658fa75d6d1da5c07eeca75645a13664dc7a341b22 \
--control-plane
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 10.5.24.32:6443 --token 4639jr.a7smqg4qwzp3tv2u \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:70b896b391bc1956dfbf6b658fa75d6d1da5c07eeca75645a13664dc7a341b22
==========================================
Follow the instruction accordingly
If you missed copying the join command, execute the following command in the master node to recreate the token with the join command.
kubeadm token create --print-join-commandCopy config to userspace bash to be able to konek kubectl/client to cluster:
$mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
$sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
$sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/configKeep this following output to execute later in worker:
(do this in worker-1 worker-2 later after Calico/CNI):
#kubeadm join 10.5.24.32:6443 --token qqo5iu.0rnk4f2rwoetyyor \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:b32b88879a91026e5ec224ab1630adb8cdbf42ba60de6e1ec7a8ee24493193e2 Verify your cluster running :
root@master-1:/home/ubuntu# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
master-1 NotReady control-plane 2m45s v1.31.2
root@master-1:/home/ubuntu# kubectl get pods -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-7c65d6cfc9-jptjm 0/1 Pending 0 30s
kube-system coredns-7c65d6cfc9-z74gm 0/1 Pending 0 32s
kube-system etcd-master-1 1/1 Running 356 2m45s
kube-system kube-apiserver-master-1 1/1 Running 348 2m45s
kube-system kube-controller-manager-master-1 1/1 Running 70 (113s ago) 2m45s
kube-system kube-proxy-mvsbd 1/1 Running 0 34s
kube-system kube-scheduler-master-1 1/1 Running 368 2m42sThe nodes will still be in “Not Ready” state until network addon ready.
Setup the pod network and metric addon
Click the add-on link from the init Master output
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
In this part we will use Calico
reference : https://docs.tigera.io/calico/latest/getting-started/kubernetes/self-managed-onprem/onpremises
in the Master node, install the operator
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.29.0/manifests/tigera-operator.yaml
###Also download custom resource to use later
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.29.0/manifests/custom-resources.yaml -O
### Customized Resource
nano custom-resources.yaml
# This section includes base Calico installation configuration.
# For more information, see: https://docs.tigera.io/calico/latest/reference/installation/api#operator.tigera.io>
apiVersion: operator.tigera.io/v1
kind: Installation
metadata:
name: default
spec:
# Configures Calico networking.
calicoNetwork:
ipPools:
- name: default-ipv4-ippool
blockSize: 26
cidr: 192.168.0.0/16
encapsulation: VXLANCrossSubnet
natOutgoing: Enabled
nodeSelector: all()
---
### IMPORTANT NOTE!!!
### If nodes are inside Openstack, use ipip encapsulation, refer to troubleshoot calico section
# This section configures the Calico API server.
# For more information, see: https://docs.tigera.io/calico/latest/reference/installation/api#operator.tigera.io>
apiVersion: operator.tigera.io/v1
kind: APIServer
metadata:
name: default
spec: {}
### Create Resource
kubectl apply -f custom-resources.yaml
### Wait until all pods running, it will takes some minutes
### Setup metric addon
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/techiescamp/kubeadm-scripts/main/manifests/metrics-server.yaml
### Check node metric
kubectl top nodesVerify and troubleshoot calico
### Install calicoctl
## Refer :https://docs.tigera.io/calico/latest/operations/calicoctl/install
## This is for operationg calico installation
curl -L https://github.com/projectcalico/calico/releases/download/v3.29.1/calicoctl-linux-amd64 -o calicoctl
chmod +x ./calicoctl
## Depends on your 'echo $PATH', copy calicoctl
mv calicoctl /usr/local/bin/
### Verifying Calico config
calicoctl get ipPool --export -o yaml > pool.yaml
cat pool.yaml
### For Openstack, Change the encapsulation to IPIP
## Also allow IP Protocols 4 and 47 in your security group
nano set-ipinip.yaml
apiVersion: projectcalico.org/v3
kind: IPPool
metadata:
name: default-ipv4-ippool
spec:
cidr: 192.168.0.0/16
ipipMode: Always
natOutgoing: true
---
save exit
kubectl replace -f set-ipinip.yaml
### Verify node status and Networking
calicoctl node status
### BGP (tcp 179) port must reachable between nodes
Sample of used security group on OpenStack
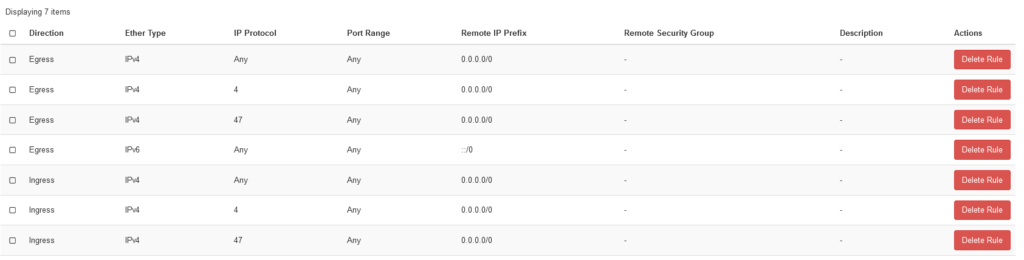
This is the #kubectl get pods -A at this stage. Make sure all are running
root@master-1:/home/ubuntu# kubectl get pods -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
calico-apiserver calico-apiserver-654d7c769b-mggb9 1/1 Running 0 5m11s
calico-apiserver calico-apiserver-654d7c769b-z7vvj 1/1 Running 2 (2m51s ago) 5m12s
calico-system calico-kube-controllers-5bc67c77b-xxwtq 1/1 Running 0 4m51s
calico-system calico-node-44nb9 1/1 Running 0 5m1s
calico-system calico-typha-645c4bcfb6-z5jkh 1/1 Running 0 5m8s
calico-system csi-node-driver-kx4gq 2/2 Running 0 4m58s
kube-system coredns-7c65d6cfc9-jptjm 1/1 Running 0 8m23s
kube-system coredns-7c65d6cfc9-z74gm 1/1 Running 0 8m25s
kube-system etcd-master-1 1/1 Running 356 10m
kube-system kube-apiserver-master-1 1/1 Running 348 10m
kube-system kube-controller-manager-master-1 1/1 Running 70 (9m46s ago) 10m
kube-system kube-proxy-mvsbd 1/1 Running 0 8m27s
kube-system kube-scheduler-master-1 1/1 Running 368 10m
tigera-operator tigera-operator-f8bc97d4c-lks6t 1/1 Running 0 6m8sAdd worker node to cluster
By the initialize Master output, you can paste the join command to the Worker node
kubeadm join 10.5.24.32:6443 --token 2ucm4t.wdqf2wcqpx0cdhia \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:618005b50326f476a0b766d4987ab95b54e3fc1a2dc295d77c5a1a0315c88357Verify the cluster
###Check Component
#kubectl get componentstatuses
###Check Node
#kubectl get node
root@node1:/home/chairul# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node1 Ready control-plane 43m v1.28.2
node2 Ready <none> 116s v1.28.2
node3 Ready <none> 98s v1.28.2
###Check Pods
#kubectl get pods -A
root@node1:/home/chairul# kubectl get pods -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-5dd5756b68-52vpg 1/1 Running 0 42m
kube-system coredns-5dd5756b68-p6cgk 1/1 Running 0 42m
kube-system etcd-node1 1/1 Running 9 (18m ago) 42m
kube-system kube-apiserver-node1 1/1 Running 7 (16m ago) 43m
kube-system kube-controller-manager-node1 1/1 Running 14 (19m ago) 42m
kube-system kube-proxy-9l2gv 1/1 Running 11 (16m ago) 42m
kube-system kube-proxy-ksvbt 1/1 Running 2 (18s ago) 113s
kube-system kube-proxy-sxkmr 1/1 Running 1 (74s ago) 95s
kube-system kube-scheduler-node1 1/1 Running 12 (19m ago) 42m
kube-system weave-net-dcfsf 2/2 Running 2 (36s ago) 95s
kube-system weave-net-vfzkf 2/2 Running 2 (55s ago) 113s
kube-system weave-net-w7k6x 2/2 Running 1 (11m ago) 11mTroubleshooting and Verification Command
###Resetting Cluster
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/setup-tools/kubeadm/kubeadm-reset/
#on master and worker
kubeadm reset
iptables -F
rm -rf /etc/cni/net.d
rm $HOME/.kube/config
reboot
###Check Component Status
#kubectl get componentstatuses
###System Journal, if kubectl failing
#sudo journalctl --since "10min ago" > all_logs.txt
###Use containerd management to inspect container of kube-system, example to check kubectl-api container
# crictl pods | grep kubectl-api
# crictl ps --pod a40aa4b396b9b
# crictl logs 0072c84f747ce |& tail -2
### Refer to this link to debug DNS Issue
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/dns-debugging-resolution/
Double check "Initialize the node parameter" part
### Use this image for troubleshoot from pod perspective
kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/admin/dns/dnsutils.yaml
kubectl exec -i -t dnsutils -- nslookup kubernetes.default
kubectl exec -i -t dnsutils -- cat /etc/resolv.conf
kubectl exec -i -t dnsutils -- ping 1.1.1.1
kubectl exec -i -t dnsutils -- nc -v 10.96.0.10 53 -u
kubectl exec -i -t dnsutils -- sh ### For interactive shell access
### Use nc -v to test connectivity
nc -v 10.96.0.10 53 -u
Connection to 10.96.0.10 53 port [tcp/domain] succeeded!
